Coding Cheat Sheets for programmers are useful to have besides. These often help us to remember various code syntax, and shortcuts and see different concepts visually. Now, ReactJS is one of the most popular frameworks for front-end development, and as it is a huge programming framework, you can’t always memorize every bit of it (especially if you’re new to this field). For that reason, we have carefully created an Ultimate Reactjs Cheatsheet for you to have a smooth experience while coding with Reactjs.
What is ReactJS?
JavaScript or JS is a common term amongst web developers. It is a scripting language that is highly used to build UI elements that make a website more assertive, responsive, and interactive. But building a functional reactive UI element that gains an appreciable user experience may seem very complex and time-consuming. That’s where Reactjs enters the game.
React is a front-end JavaScript library that helps us create UI components without hassle. These components are also reusable so sometimes if we are lucky enough we may not need to write code at all. It is a UI Component Library that only works in our application’s view layer.
ReactJS Cheatsheet
Here, you will find the ultimate Reactjs cheatsheet for 2022.

New Features
Automatic Batching
// Before: only React events were batched.
setTimeout(() => {
setCount(c => c + 1);
setFlag(f => !f);
// React will render twice, once for each state update (no batching)
}, 1000);
// After: updates inside of timeouts, promises,
// native event handlers or any other event are batched.
setTimeout(() => {
setCount(c => c + 1);
setFlag(f => !f);
// React will only re-render once at the end (that's batching!)
}, 1000);
Returning Multiple Elements
You can return multiple elements as arrays or fragments.
Arrays
render () {
// Don't forget the keys!
return [
<li key="A">First item</li>,
<li key="B">Second item</li>
]
}
Fragments
render () {
// Fragments don't require keys!
return (
<Fragment>
<li>First item</li>
<li>Second item</li>
</Fragment>
)
}
Returning Strings
render() {
return 'Look ma, no spans!';
}
You can return just a string.
Errors
class MyComponent extends Component {
···
componentDidCatch (error, info) {
this.setState({ error })
}
}
Catch errors via componentDidCatch. (React 16+)
Portals
render () {
return React.createPortal(
this.props.children,
document.getElementById('menu')
)
}
This renders this.props.children into any location in the DOM.
Hydration
const el = document.getElementById('app');
ReactDOM.hydrate(<App />, el);
Use ReactDOM.hydrate instead of using ReactDOM.render if you’re rendering over the output of ReactDOMServer.
Hooks
State Hook
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Example() {
// Declare a new state variable, which we'll call "count"
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
}
Declaring Multiple State Variables
function ExampleWithManyStates() {
// Declare multiple state variables!
const [age, setAge] = useState(42);
const [fruit, setFruit] = useState('banana');
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([{ text: 'Learn Hooks' }]);
// ...
}
Effect Hook
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function Example() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
// Similar to componentDidMount and componentDidUpdate:
useEffect(() => {
// Update the document title using the browser API
document.title = `You clicked ${count} times`;
}, [count]);
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
}
Building Your Hooks
Define FriendStatus
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
function FriendStatus(props) {
const [isOnline, setIsOnline] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
function handleStatusChange(status) {
setIsOnline(status.isOnline);
}
ChatAPI.subscribeToFriendStatus(props.friend.id, handleStatusChange);
return () => {
ChatAPI.unsubscribeFromFriendStatus(props.friend.id, handleStatusChange);
};
}, [props.friend.id]);
if (isOnline === null) {
return 'Loading...';
}
return isOnline ? 'Online' : 'Offline';
}
Use FriendStatus
function FriendStatus(props) {
const isOnline = useFriendStatus(props.friend.id);
if (isOnline === null) {
return 'Loading...';
}
return isOnline ? 'Online' : 'Offline';
}
Components
Components
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class Hello extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div className="message-box">Hello {this.props.name}</div>;
}
}
const el = document.body;
ReactDOM.render(<Hello name="John" />, el);
Use the React.js jsfiddle or the unofficial jsbin to start hacking.
Import Multiple Exports
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class Hello extends Component {
...
}
Properties
<video fullscreen="{true}" autoplay="{false}" />
render () {
this.props.fullscreen
const { fullscreen, autoplay } = this.props
···
}
Use this.props to access properties passed to the component.
States
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = { username: undefined }
}
this.setState({ username: 'rstacruz' });
render () {
this.state.username
const { username } = this.state
···
}
Use states (this.state) to manage dynamic data.
With Babel, you can use proposal-class-fields and get rid of constructor
class Hello extends Component {
state = { username: undefined };
...
}
Nesting
class Info extends Component {
render() {
const { avatar, username } = this.props;
return (
<div>
<UserAvatar src={avatar} />
<UserProfile username={username} />
</div>
);
}
}
Now, fragments can be used to return multiple children without adding extra wrapping nodes to the DOM.
import React, { Component, Fragment } from 'react';
class Info extends Component {
render() {
const { avatar, username } = this.props;
return (
<Fragment>
<UserAvatar src={avatar} />
<UserProfile username={username} />
</Fragment>
);
}
}
Children
<AlertBox>
<h1>You have pending notifications</h1>
</AlertBox>
class AlertBox extends Component {
render() {
return <div className="alert-box">{this.props.children}</div>;
}
}
Children are passed as the children property.
Defaults
Setting Default Props
Hello.defaultProps = {
color: 'blue',
};
Setting Default State
class Hello extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { visible: true };
}
}
Set the default state in the constructor().
And without constructor using Babel with proposal-class-fields.
class Hello extends Component {
state = { visible: true };
}
Other Components
Functional components
function MyComponent({ name }) {
return <div className="message-box">Hello {name}</div>;
}
Functional components have no state. Also, their props are passed as the first parameter to a function.
Pure components
import React, {PureComponent} from 'react'
class MessageBox extends PureComponent {
···
}
Performance-optimized version of React.Component. Doesn’t rerender if props/state hasn’t changed.
Component API
this.forceUpdate();
this.setState({ ... })
this.setState(state => { ... })
this.state;
this.props;
These methods and properties are available for Component instances.
DOM Nodes
References
class MyComponent extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<input ref={(el) => (this.input = el)} />
</div>
);
}
componentDidMount() {
this.input.focus();
}
}
Allows access to DOM nodes.
DOM Events
class MyComponent extends Component {
render() {
<input type="text" value={this.state.value} onChange={(event) => this.onChange(event)} />;
}
onChange(event) {
this.setState({ value: event.target.value });
}
}
Pass functions to attributes like onChange.
Other Features
Transferring Props
<VideoPlayer src="video.mp4" />
class VideoPlayer extends Component {
render() {
return <VideoEmbed {...this.props} />;
}
}
Propagates src="..." down to the sub-component.
Top-level API
React.createClass({ ... })
React.isValidElement(c)
ReactDOM.render(<Component />, domnode, [callback]);
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(domnode);
ReactDOMServer.renderToString(<Component />);
ReactDOMServer.renderToStaticMarkup(<Component />);
There are more, but these are the most common.
JSX patterns
Style Shorthand
const style = { height: 10 };
return <div style={style}></div>;
return <div style={{ margin: 0, padding: 0 }}></div>;
Inner HTML
function markdownify() {
return '<p>...</p>';
}
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: markdownify() }} />;
Lists
class TodoList extends Component {
render() {
const { items } = this.props;
return (
<ul>
{items.map((item) => (
<TodoItem item={item} key={item.key} />
))}
</ul>
);
}
}
Always supply a key property.
Conditionals
<Fragment>{showMyComponent ? <MyComponent /> : <OtherComponent />}</Fragment>
Short-Circuit Evaluation
<Fragment>
{showPopup && <Popup />}
...
</Fragment>
Property Validation
PropTypes
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
Basic Types
MyComponent.propTypes = {
email: PropTypes.string,
seats: PropTypes.number,
callback: PropTypes.func,
isClosed: PropTypes.bool,
any: PropTypes.any,
};
Required Types
MyCo.propTypes = {
name: PropTypes.string.isRequired,
};
Elements
MyCo.propTypes = {
// React element
element: PropTypes.element,
// num, string, element, or an array of those
node: PropTypes.node,
};
Enumerables (oneOf)
MyCo.propTypes = {
direction: PropTypes.oneOf(['left', 'right']),
};
Arrays and Objects
MyCo.propTypes = {
list: PropTypes.array,
ages: PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.number),
user: PropTypes.object,
user: PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.number),
message: PropTypes.instanceOf(Message),
};
MyCo.propTypes = {
user: PropTypes.shape({
name: PropTypes.string,
age: PropTypes.number,
}),
};
Use .array[Of], .object[Of], .instanceOf, .shape.
Custom Validation
MyCo.propTypes = {
customProp: (props, key, componentName) => {
if (!/matchme/.test(props[key])) {
return new Error('Validation failed!');
}
},
};
Wrapping Up
Your search for Reactjs Cheatsheet appears to have ended. Coding with React and remembering all of its code snippets is a long period of work. It will take time, but sticking to its guidelines, cheatsheets, and roadmaps will help you stay ahead of the game in the long run.
Similar ReactJS Blogs from UI-Lib
- General React JS Interview Questions To Land Your Next Job
- React Boilerplates You Should Not Miss
- Top ReactJS Table Libraries
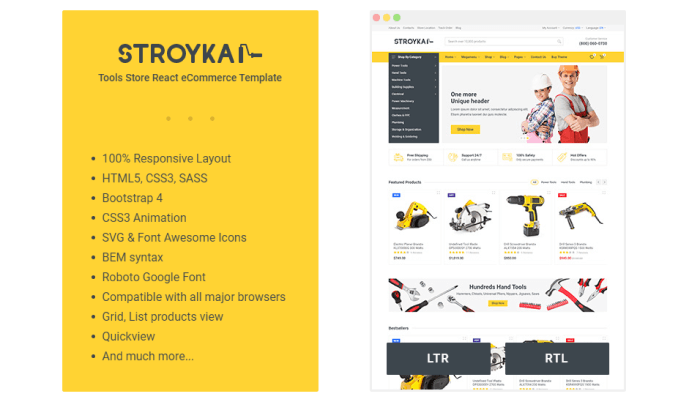
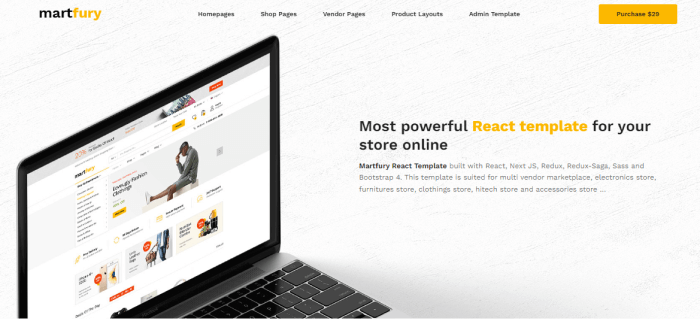
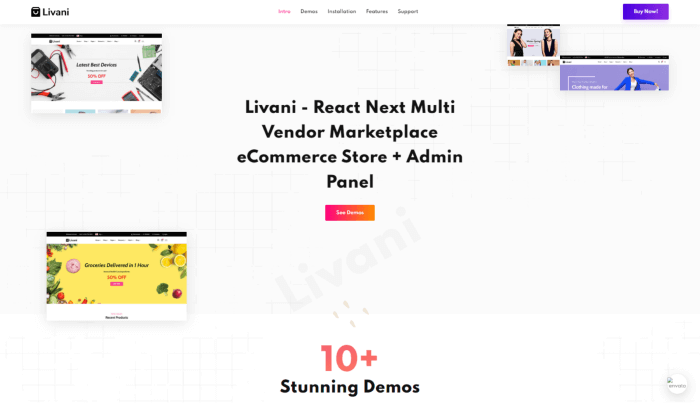
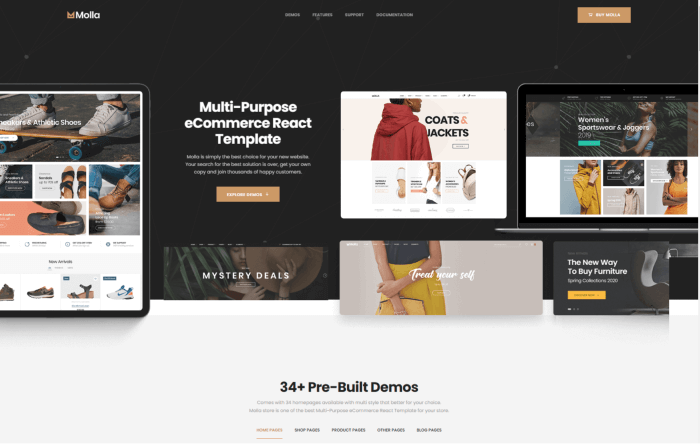
- Best React eCommerce Templates
- Best Free React Admin Templates
- Free & Premium React Portfolio Templates
- Free Best React Date Picker Components
- Top React Static Site Generators
- React Landing Page Templates
- Admin Templates with ReactJS
- Tools for a React Landing Page Template